Suicide prevention for older adults is an urgent issue that demands immediate attention. Research reveals that seniors, particularly those aged 75 and above, face the highest suicide rates of any demographic, underscoring the critical need for effective mental health resources tailored to this age group. Despite the increasing number of older adults turning to online platforms for support, existing suicide prevention initiatives often overlook their specific needs. The study conducted by researchers at McLean Hospital highlights the stark imbalance in targeted resources, stressing that elderly mental health requires comprehensive solutions that are easily accessible. To combat these alarming trends, the call for enhanced geriatric psychiatry practices and online suicide prevention campaigns aimed at our seniors is more necessary than ever.
Addressing the daunting issue of suicide among senior citizens is vital for enhancing public health. This demographic, especially those in late adulthood, experiences a profound prevalence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors, pointing to a significant gap in available support systems. Notably, the growing trend of social isolation among older individuals exacerbates these mental health challenges, necessitating a more focused approach to intervention. Furthermore, the historical underrepresentation of older adults in mental health research calls for tailored strategies that recognize their unique experiences and emotional needs. By prioritizing targeted campaigns and interventions, we can work towards reducing senior suicide rates and fostering a more supportive environment for our aging population.
Understanding Senior Suicide Rates
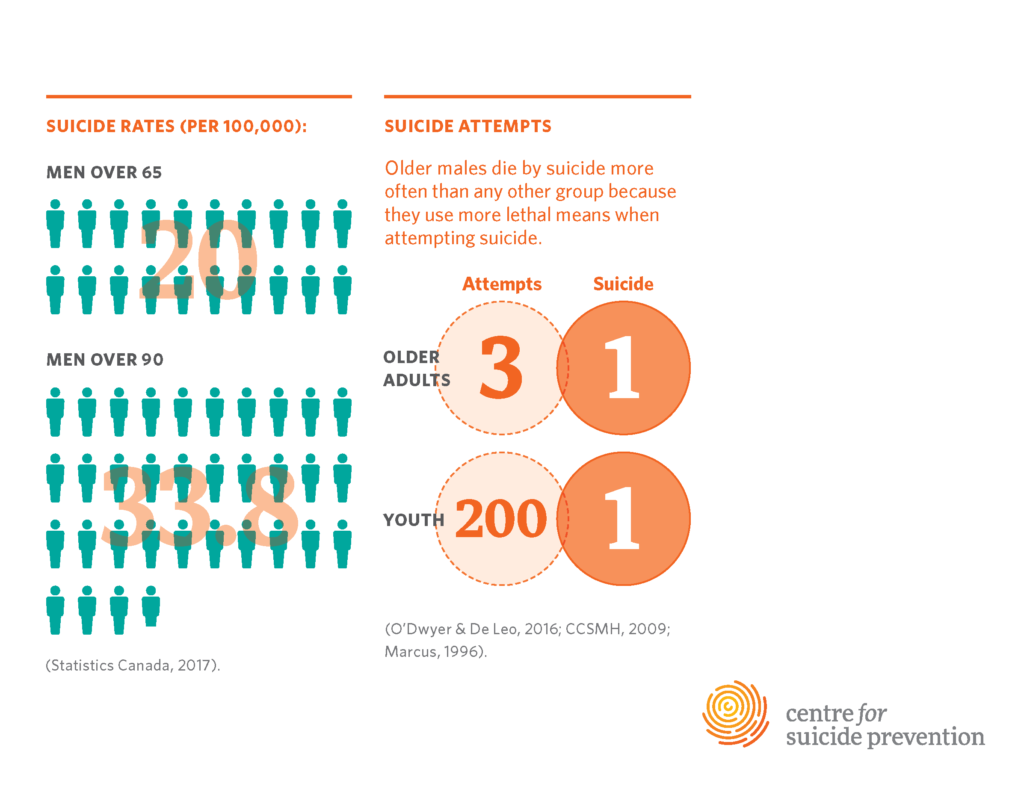
Suicide rates among older adults have reached alarming levels, particularly in the cohort of those aged 75 and over who report a staggering rate of 20.3 per 100,000, as noted by the CDC. This demographic is often neglected when it comes to resources and support for mental health issues. Various factors contribute to this situation, including social isolation, chronic health conditions, and limited access to mental health resources. Addressing these factors is crucial in our efforts to reduce the alarming rates of suicide in older adults.
Compounding the issue is the lack of representation in mental health research that focuses on older populations. This gap has led to disparities in effective interventions that can address elderly mental health concerns. Many elder-focused mental health resources are either hard to find or not tailored to the unique needs of older adults. As such, public health campaigns need to pivot their strategies by incorporating specific initiatives that directly tackle the crisis of senior suicide rates.
Important Mental Health Resources for Older Adults
Mental health resources for older adults should be more accessible and explicitly targeted toward the unique challenges faced by this population. There is a clear need for tailored support that considers the experiences of loneliness, loss of loved ones, and declining health that many older adults face. Comprehensive resources must include information on both local and online suicide prevention programs, encouraging seniors to seek help when they need it. Furthermore, organizations need to leverage technology to create online platforms that cater specifically to older adults.
In addition to traditional mental health resources, integrating community support into these efforts can enhance efficacy. Programs such as peer support groups, online counseling tailored for elderly individuals, and outreach efforts in senior centers can bridge the gap in mental health support. Importantly, by creating awareness around the availability of these resources, older adults may feel more empowered to seek assistance and navigate their mental health challenges.
The Role of Geriatric Psychiatry in Suicide Prevention
Geriatric psychiatry plays a pivotal role in addressing the mental health needs of older adults, particularly when it comes to suicide prevention. Professionals in this field are well-equipped to understand the unique bio-psycho-social factors influencing mental health in seniors. They are armed with strategies that cater to the mental health resources required by older adults, fostering an environment where these individuals can openly discuss their feelings and challenges without stigma.
Moreover, the integration of geriatric psychiatry into mainstream healthcare can help identify at-risk individuals earlier. By focusing on preventative care and early intervention, psychiatrists can develop tailored strategies that assist older adults in managing their mental health. This could involve employing evidence-based therapies or medication management that respects the complexities of aging and mental health, ultimately aiming to lower the rates of suicide among older populations.
Addressing Social Isolation in Older Adults
Social isolation is a critical factor contributing to the heightened risk of suicide amongst older adults. As individuals age, they often experience the loss of friends and loved ones, leading to a profound sense of loneliness. This emotional state can exacerbate mental health issues, making it imperative to create programs that connect older adults with their peers. Efforts to combat social isolation could include community engagement activities, online support groups, and resource-sharing platforms.
By fostering connections through both online and offline initiatives, there’s a greater chance to provide emotional support that may deter suicidal ideations. Furthermore, community centers and organizations can play an active role in reducing isolation by promoting social events tailored for seniors and encouraging participation in various activities that stimulate mental engagement and interactions.
Harnessing Technology for Online Suicide Prevention
In an era where technology is paramount, online suicide prevention resources have proven to be a valuable tool. However, it was found that older adults face challenges in accessing these resources due to poor digital literacy or lack of targeted content. To better serve this population, it is imperative that online platforms are designed with user-friendliness in mind and specifically address the types of support older adults seek. This includes offering video tutorials on navigating mental health resources available online.
Innovative uses of technology, such as virtual reality therapy and telepsychiatry, can bridge the gap between older adults and mental health support. They not only offer immediate access to help but also empower seniors to manage their mental health from the comfort of their homes. Such advancements in online suicide prevention can significantly impact the mental wellness of older adults, ultimately helping to reduce the alarming rates of suicide in this demographic.
Call for Increased Funding in Elderly Mental Health
The dire need for more funding focused on elderly mental health is underscored by current trends in senior suicide rates. With limited resources and a growing population of older adults, there is an urgent call for increased investments in mental health programs that address late-life issues. Financial backing for research in geriatric psychiatry is essential to develop effective mental health resources and interventions designed for older adults.
Funding has the potential to create innovative mental health initiatives that can directly reduce the incidence of suicide in seniors. By prioritizing budget allocations for programs dedicated to mental health screenings, public awareness campaigns, and community-based support systems tailored for older adults, stakeholders can create a solid foundation for a comprehensive approach to suicide prevention in this vulnerable age group.
Implementation of Tailored Suicide Prevention Campaigns
Implementing tailored suicide prevention campaigns for older adults is essential in tackling the unique challenges they face. These campaigns should be designed based on thorough research, examining the specific mental health needs and barriers within the elderly population. Effective messaging that resonates with older adults, using relatable stories and appropriate language, will significantly enhance the outreach and effectiveness of these campaigns.
Moreover, involving older adults in the development of these campaigns—from design to implementation—ensures that the resources meet their needs and preferences. By emphasizing the importance of mental health and illustrating available resources, communities can foster more supportive environments that encourage older adults to seek help before reaching a crisis stage.
Collaborative Efforts Between Organizations
Collaborative efforts between various organizations and stakeholders are crucial in enhancing suicide prevention strategies for older adults. By combining resources and expertise from mental health agencies, geriatric care programs, and nonprofit organizations, a more comprehensive and effective approach can be developed. This collaboration can promote the sharing of best practices and facilitate access to critical resources, ultimately improving the impact on older adult mental health.
These partnerships can create synergies that boost funding opportunities and drive innovative solutions to common challenges faced by seniors. Joint campaigns can benefit from targeted outreach efforts that emphasize the importance of mental health resources tailored for older adults, thereby addressing the imbalances currently existing in suicide prevention resources available to this population.
Raising Awareness and Education on Suicide Among Seniors
Raising awareness about suicide among older adults is key in driving change within communities and institutions. Increasing public awareness can help dismantle the stigma surrounding mental health discussions for older adults, encouraging them and their families to engage in open conversations. Educational programs that inform the community about the signs of mental health struggles in seniors, ensuring that friends and family can seek help on their behalf, can play a pivotal role in suicide prevention.
Education should also extend to healthcare providers and policymakers to improve the ways in which they engage with older adults regarding mental health. Training in geriatric mental health issues can help health professionals identify at-risk individuals and empower them with the knowledge to connect these seniors with appropriate mental health resources and support.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key mental health resources for suicide prevention for older adults?
Key mental health resources for suicide prevention for older adults include hotlines like the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline, which offers free and confidential support. Additionally, organizations such as AARP provide information tailored to senior mental health. Community centers and geriatric psychiatry clinics can also be vital places for older adults to find support tailored to their specific needs.
How do senior suicide rates compare to those of younger populations?
Senior suicide rates, particularly for adults aged 75 and older, are significantly higher than those of younger populations. According to the CDC, the suicide rate for this age group is 20.3 per 100,000, highlighting an urgent need for targeted suicide prevention for older adults, as rates have risen in this demographic while they have declined among younger individuals.
What unique factors contribute to elderly mental health and suicide risks?
Elderly mental health is often affected by factors such as social isolation, chronic health issues, loss of loved ones, and a lack of mental health resources. These factors collectively contribute to increased suicide risks among older adults, necessitating a focus on tailored support and online suicide prevention efforts to address their specific challenges.
How can online suicide prevention resources be improved for older adults?
Improving online suicide prevention resources for older adults involves creating easily accessible websites with clear information specifically designed for seniors. This includes using larger fonts, simplified navigation, and ensuring that content addresses the unique mental health concerns faced by older adults, thus making it easier for them to find critical support.
What role does geriatric psychiatry play in suicide prevention for seniors?
Geriatric psychiatry plays a crucial role in suicide prevention for seniors by providing specialized care tailored to the mental health needs of older adults. Professionals in this field understand the unique challenges faced by elderly individuals and can develop targeted interventions that focus on improving mental health outcomes and reducing suicide risks.
Are there specific signs of suicidal thoughts in older adults that family members should look for?
Family members should be aware of signs such as withdrawal from social activities, changes in mood, expressions of hopelessness, and any direct talk about wanting to die. Recognizing these early warning signs can be critical for timely suicide prevention for older adults.
What community resources are available for online suicide prevention for older adults?
Community resources for online suicide prevention for older adults include outreach programs, local mental health hotlines, and community support groups that specifically cater to seniors. Many health organizations also offer virtual workshops or webinars focused on mental health, emphasizing the importance of accessible support in the digital age.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| High Risk Population | Older adults, especially those aged 75 and over, have the highest suicide rates compared to other age groups. |
| Lack of Resources | National suicide prevention organizations offer few resources specifically targeting older adults. |
| Research Findings | A study published in the American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry highlighted the imbalance of resources and immediate need for better online access for older adults. |
| Causes of High Rates | Increased social isolation, underrepresentation in research, and biases against older adults contribute to rising suicide rates. |
| Next Steps | Targeted suicide prevention campaigns and more funding for late-life research are essential to address these issues. |
Summary
Suicide prevention for older adults has become an urgent public health concern, particularly for those aged 75 and above, who are at the highest risk. It is crucial to recognize that although this demographic faces significant threats, the resources available to them are woefully inadequate. Comprehensive research has shown that older adults often feel isolated and struggle with finding access to suitable support systems, highlighting the necessity for more targeted suicide prevention efforts. With an increase in awareness and tailored campaigns, we can help ensure that older individuals receive the care and resources they need, significantly reducing the rates of suicide in this vulnerable population.