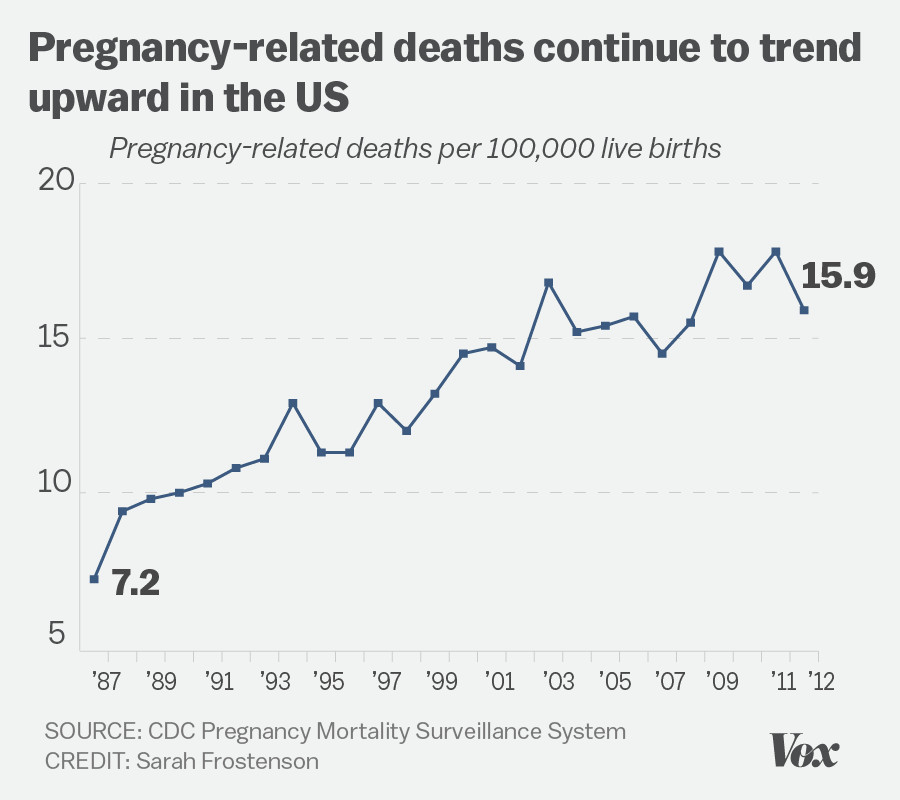
In recent years, U.S. pregnancy-related deaths have become a pressing public health crisis, with the maternal mortality rate remaining the highest among high-income countries. Alarmingly, studies indicate that over 80 percent of these pregnancy-related deaths are preventable, emphasizing the need for urgent reforms in prenatal and postpartum care. The disparities highlighted in maternal health across different racial and ethnic groups reveal profound healthcare system inequities, mandating immediate policy interventions. Notably, American Indian and Alaska Native women face strikingly high mortality rates, nearly four times that of their white counterparts. Addressing these preventable pregnancy deaths requires not only better resources during pregnancy but also comprehensive strategies to support women’s health across the entire postpartum period.
The issue of maternal mortality in the United States has garnered increasing attention, as pregnancy-related fatalities continue to escalate. This alarming trend highlights the urgent need to address preventable deaths that disproportionately affect marginalized communities, unveiling stark racial disparities in maternal health outcomes. Research suggests that systemic inequities within the healthcare system, including inadequate access to quality care, exacerbate these challenges. Furthermore, as many individuals face long-term health complications after childbirth, the importance of comprehensive postpartum care cannot be overstated. Bridging these gaps in maternal healthcare is essential to ensure that all women have the opportunity to thrive before, during, and after pregnancy.
Understanding U.S. Pregnancy-Related Deaths
The alarming rise in U.S. pregnancy-related deaths has placed a spotlight on the need for immediate reforms in maternal healthcare. As noted in recent studies, over 80 percent of these deaths are preventable, and yet the United States continues to have the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries. Factors contributing to this crisis include significant healthcare system inequities, lack of access to quality prenatal care, and extensive disparities among racial and ethnic groups. Addressing these issues is crucial for reversing this tragic trend.
Research indicates that from 2018 to 2022, the maternal mortality rate in the U.S. saw alarming increases, particularly among American Indian and Alaska Native women, who face mortality rates nearly four times greater than their white counterparts. This discrepancy highlights the urgent need for targeted interventions and policies that can bridge the gap in maternal health outcomes. If significant changes are not made, the upward trend in preventable pregnancy deaths is likely to continue.
Although the national statistics are troubling, they also reveal specific areas where improvements can be made. For instance, states like California have successfully lowered their maternal mortality rates and serve as a model for others. If national averages reflected the best-performing states, thousands of lives could be saved annually. It underscores the necessity for best practice sharing among states and addressing the unique challenges faced in different regions.
Ultimately, reducing U.S. pregnancy-related deaths will require a multifaceted approach that focuses not only on immediate healthcare access but also on the underlying systemic factors that contribute to maternal mortality. It is essential for policymakers, healthcare providers, and communities to collaborate on solutions that address maternal care comprehensively.
Maternal Mortality Rate in Context
The maternal mortality rate (MMR) in the U.S. presents a stark reality when compared to other high-income nations. While many countries have made substantial progress in decreasing their MMR, the U.S. has stagnated or even regressed in certain areas. The factors contributing to this are complex and include societal, economic, and healthcare system inequities. Key issues such as limited access to prenatal care and a fragmented healthcare system exacerbate the situation and undermine efforts to reduce preventable pregnancy deaths.
Additionally, chronic health conditions—particularly cardiovascular disease—are increasingly emerging as leading causes of maternal mortality. This trend indicates a critical need for better screening and management of chronic issues during the pregnancy and postpartum periods. Addressing maternal health holistically is vital, as women often experience increased health complications both during and after their pregnancies.
The Role of Racial Disparities in Maternal Health
Racial disparities in maternal health continue to be a significant concern in the U.S., with non-Hispanic Black and American Indian women facing disproportionately high maternal mortality rates. Factors such as systemic racism, economic instability, and access to healthcare contribute to these disparities, resulting in a healthcare experience that varies drastically based on race and geography. Understanding these inequities is crucial to forming targeted interventions that promote health equity.
Efforts to reduce racial disparities in maternal health have gained momentum, yet the reality is that meaningful change has yet to materialize across the board. Ongoing bias in healthcare settings and chronic underfunding of maternal health services must be addressed to create an environment where all women receive the care they deserve. By focusing on both policy reform and community support, stakeholders can champion maternal health equity.
Healthcare System Inequities and Their Impact
Healthcare system inequities play a critical role in the rising maternal mortality rate in the U.S. A patchwork system often leads to fragmented care, where women may not receive continuous support from prenatal through postpartum. In many areas, maternity care deserts—regions with insufficient healthcare providers—create barriers for expectant mothers, limiting their access to vital services that could prevent complications.
Addressing these inequities requires a concerted effort to redesign the healthcare system with a focus on inclusivity and patient-centered care. Policymakers and healthcare providers must prioritize resources to underserved areas and improve healthcare access for marginalized groups. This transformation will not happen without strategic planning and sustained investment, both of which are essential for reducing maternal mortality rates across the nation.
Postpartum Care: A Critical Component
Postpartum care is often overlooked yet is a critical component of maternal health that can significantly influence mortality rates. Many maternal fatalities occur not during childbirth but rather in the months following delivery, pointing to an urgent need for comprehensive postpartum systems. Support during this period is essential for addressing potential complications such as hypertension and mental health issues, which are commonly seen in new mothers.
Expanding postpartum care initiatives can provide crucial education and resources to ensure mothers receive proper follow-up care and management of any chronic conditions. It is vital for healthcare systems to recognize that the transition into motherhood extends well beyond the birth event. Providing ongoing support and resources during the postpartum period plays a key role in reducing overall maternal mortality and improving health outcomes for mothers.
Strategies to Improve Maternal Health Outcomes
To effectively tackle the growing crisis of maternal mortality in the U.S., it is essential to adopt evidence-based strategies that focus on enhancing maternal health outcomes. This includes investing in healthcare infrastructure, prioritizing research on maternal health disparities, and developing community-based programs that cater to the unique needs of expectant and new mothers. Policymakers must become advocates for change, promoting policies that guarantee access to quality care.
Moreover, public health campaigns aimed at raising awareness about maternal health risks and the importance of early interventions can empower women to seek appropriate care during pregnancy and postpartum. By leveraging technology and community health resources, stakeholders can make strides in reducing preventable pregnancy deaths and ensuring that all women have access to safe and effective maternal healthcare.
Innovations in Maternal Healthcare
Innovations in maternal healthcare present promising solutions to address the rising rates of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. Health tech advancements, such as telehealth services and mobile health applications, have the potential to increase access to quality care, especially in remote areas. These technologies can help bridge gaps in communication and education for expectant mothers, enabling them to make informed decisions regarding their health.
Furthermore, maternal health-focused initiatives that encourage collaboration amongst healthcare providers, policymakers, and community organizations can foster comprehensive approaches to care. By sharing best practices and leveraging data-driven insights, stakeholders can create systematic changes necessary to combat disparities and enhance maternal health across diverse populations.
The Need for Data-Driven Solutions
The tracking of maternal mortality in the U.S. has improved since the implementation of pregnancy checkboxes on death certificates, yet comprehensive data collection remains a challenge. Strengthening the systems used to gather, analyze, and report maternal health data is crucial for identifying trends, understanding disparities, and tailoring interventions to address specific needs. A robust national database would enable stakeholders to respond quickly to emerging issues in maternal health.
Investing in maternal health research is vital for developing effective strategies aimed at reducing preventable pregnancy deaths. By funding studies that center on racial disparities and healthcare system inefficiencies, we can gain insight into the factors contributing to these inequalities and develop targeted solutions. Long-term commitment to data-driven public health initiatives can help guide policy decisions and improve health outcomes for mothers across the U.S.
Advocacy and Community Support for Maternal Health
Advocacy plays a pivotal role in advancing maternal health issues and addressing the alarming rates of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. Grassroots movements spearheaded by community organizations can help amplify the voices of women who have been disproportionately affected by adverse health outcomes. Mobilizing these efforts around public policy changes can lead to improved access to maternal healthcare services.
Additionally, community support systems are essential in fostering an inclusive environment where women are encouraged to seek care and share their experiences. Networks of support can lead to better health literacy and empower mothers to advocate for their own needs within the healthcare system. Ultimately, a combined effort of advocacy, education, and community engagement can drive meaningful change and enhance maternal health outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of rising U.S. pregnancy-related deaths?
U.S. pregnancy-related deaths continue to rise due to several factors, primarily including cardiovascular disease, healthcare system inequities, and preventable pregnancy deaths linked to inadequate prenatal and postpartum care. The U.S. maternal mortality rate is highest among high-income countries, highlighting the urgent need for systematic improvements in healthcare policies and access.
How do racial disparities affect maternal mortality rates in the U.S.?
Racial disparities significantly impact maternal mortality rates in the U.S., with American Indian and Alaska Native women facing the highest rates at 106.3 deaths per 100,000 live births compared to 27.6 for white women. These disparities arise from systemic bias, inequitable healthcare access, and chronic conditions, underscoring the need for targeted interventions to address these healthcare system inequities.
What percentage of U.S. pregnancy-related deaths are preventable?
More than 80% of U.S. pregnancy-related deaths are preventable. This alarming statistic emphasizes the necessity for enhanced maternity care support and effective public health strategies to improve outcomes and reduce preventable pregnancy deaths.
Why is extended postpartum care critical in reducing maternal mortality rates?
Extended postpartum care is vital as many pregnancy-related deaths occur between 42 days to 1 year after pregnancy. Improving support during this period can significantly impact maternal health, ensuring that complications like hypertension and mental health issues are addressed, thereby decreasing overall maternal mortality.
How does the U.S. maternal mortality rate compare to other high-income countries?
The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, emphasizing the need for urgent reforms in healthcare practices and policies. From 2018 to 2022, rates have increased, illustrating ongoing challenges in providing equitable and effective maternity care across the nation.
What role does healthcare system design play in U.S. maternal mortality?
The design of the U.S. healthcare system, characterized by a patchwork of services and inequities, contributes significantly to maternal mortality. Issues such as insufficient access to care, especially in maternity care deserts, lead to higher rates of pregnancy-related deaths among vulnerable populations.
What changes are needed to improve maternal health outcomes in the U.S.?
To improve maternal health outcomes in the U.S., it is essential to invest in public health infrastructure, enhance quality of care during pregnancy, focus on postpartum support, and address state-level policy differences that contribute to disparities in maternal mortality rates.
What measures can be taken to address healthcare system inequities impacting maternal health?
Measures to address healthcare system inequities include policy reforms aimed at increasing access to quality maternity care, implementing training programs to reduce bias among healthcare providers, and fostering community health initiatives to better serve marginalized groups at higher risk for maternal mortality.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Preventability | More than 80% of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are preventable. |
| Maternal Mortality Rate | The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries and it has risen from 25.3 to 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births between 2018 and 2022. |
| Racial Disparities | American Indian and Alaska Native women have the highest rates (106.3 deaths per 100,000 live births), followed by non-Hispanic Black women (76.9) and white women (27.6). |
| Impact of COVID-19 | The sharpest increase in maternal mortality rates occurred in 2021, likely due to the COVID-19 pandemic. |
| Leading Cause of Death | Cardiovascular disease is now the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths. |
| Late Maternal Deaths | Late maternal deaths (deaths between 42 days to one year postpartum) account for nearly a third of all pregnancy-related deaths. |
| Need for Policy Change | There is a need for better prenatal care, postpartum care, and addressing inequities in healthcare across different states. |
| Public Health Investment | There is a call for increased investment in public health infrastructure to improve maternal health outcomes. |
Summary
U.S. pregnancy-related deaths are a growing concern, as the nation continues to experience the highest maternal mortality rates among high-income countries. A recent study highlights that more than 80 percent of these deaths are preventable, yet disparities persist across racial and geographic lines. The rise in mortality rates from 2018 to 2022 underscores the urgent need for systemic changes in healthcare, particularly in addressing the lack of prenatal and extended postpartum care. To improve outcomes, it is essential to invest in public health infrastructure and equitable health policies that prioritize maternal health for all women.