TIM-3 therapy for Alzheimer’s is emerging as a revolutionary approach that harnesses the immune system’s capabilities to combat the debilitating effects of this progressive neurodegenerative condition. Recent research has uncovered that by targeting the TIM-3 immune checkpoint, scientists are able to reactivate microglia—critical immune cells in the brain—allowing them to clear plaque deposits that contribute to cognitive decline. This innovative therapy not only offers hope for Alzheimer’s treatment but also sheds light on the intricate relationship between neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s disease progression. In studies with mouse models, the removal of TIM-3 resulted in significantly improved memory and cognitive function, marking a potential breakthrough in the field of Alzheimer’s research. As we explore the implications of TIM-3 therapy, we are witnessing a promising intersection of cancer treatment strategies and the quest for effective Alzheimer’s interventions.
The quest for effective Alzheimer’s therapies has taken a fascinating turn with the introduction of TIM-3 as a pivotal target. This immune checkpoint molecule, traditionally associated with cancer, has now been recognized for its role in modulating the brain’s immune response. By inhibiting TIM-3, researchers are unlocking new pathways for microglia to engage with and reduce harmful amyloid plaques that accumulate in the aging brain. This novel perspective on the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease underscores the importance of neuroinflammation and how immune mechanisms can be repurposed to facilitate cognitive recovery. Ultimately, TIM-3 therapy represents a beacon of hope for those affected by Alzheimer’s, as it combines cutting-edge immunology with insights gleaned from cancer research to pave the way for innovative treatment options.
Understanding TIM-3 Therapy for Alzheimer’s Disease
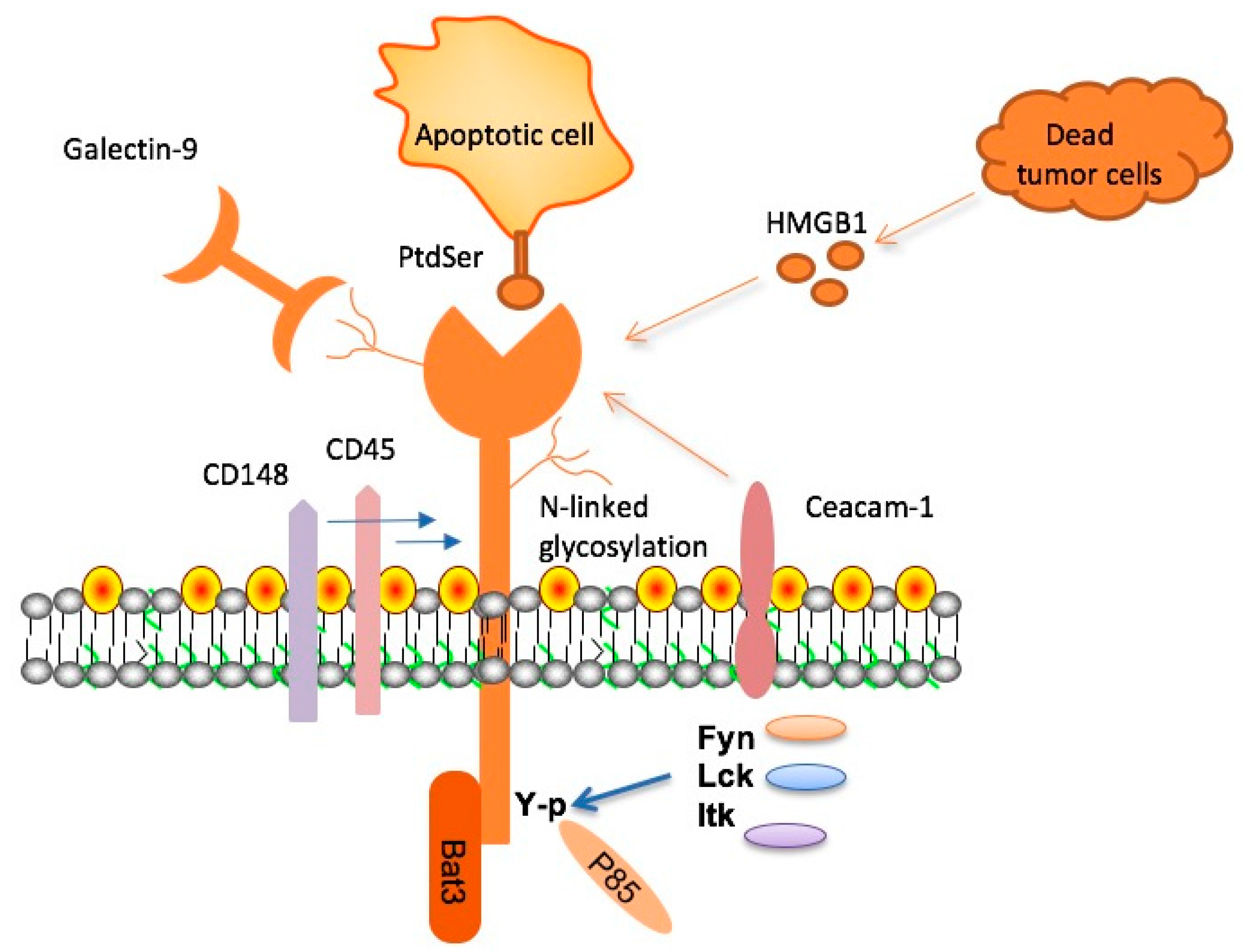
Recent advances in Alzheimer’s treatment have highlighted the potential of TIM-3 therapy as a groundbreaking approach. TIM-3, or T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin-domain-containing protein 3, plays a role in the regulation of immune responses. By inhibiting the action of this immune checkpoint, researchers are investigating its ability to rejuvenate immune cells called microglia in the brain. Microglia are essential for clearing amyloid plaques, which accumulate in the brains of Alzheimer’s patients and contribute to neurodegeneration. By turning off TIM-3, microglia can be freed to carry out their critical function and potentially restore cognitive function.
The findings from recent studies suggest that TIM-3 therapy may alter the behavior of toxic plaques. In experiments conducted on mice where the TIM-3 gene was deleted, an increase in microglial activity was observed, leading to improved memory and learning capabilities. This form of therapy holds promise as a new strategy in combating neuroinflammation associated with Alzheimer’s disease, offering a fresh perspective after numerous challenges faced in traditional treatment approaches. Harnessing TIM-3 as a therapeutic target opens avenues for more effective Alzheimer’s treatment.
The Role of Microglia in Alzheimer’s Disease
Microglia serve as the primary immune defense in the brain, their functions extending beyond mere protection against pathogens. In healthy brains, microglia are involved in synaptic pruning, enhancing memory formation by removing unneeded synapses. However, in the context of Alzheimer’s disease, these microglia become dysfunctional, primarily due to increased expression of molecules like TIM-3. This phenomenon leads to a failure in clearing harmful amyloid beta plaques, ultimately exacerbating neurodegenerative processes.
As age progresses, and particularly in Alzheimer’s patients, the homeostatic state of microglia changes due to TIM-3’s inhibitory effects. Rather than engaging in plaque clearance, these cells become static, unable to respond to the accumulation of amyloid beta. This condition results in chronic inflammation and cognitive decline, emphasizing the critical role microglia play in the pathology of Alzheimer’s. Addressing microglial dysfunction through novel treatments targeting TIM-3 could be pivotal in restoring cognitive health in affected individuals.
Implications of Cancer Treatment Strategies in Alzheimer’s Care
The interplay between cancer treatment strategies and Alzheimer’s care showcases a remarkable opportunity to leverage immune therapies across different diseases. The mechanism underlying TIM-3’s role in inhibiting immune responses has been exploited in various cancer treatments. These therapies have unraveled how checkpoint inhibitors can nudge the immune system into action, an insight now being directed towards Alzheimer’s treatment. By adapting such strategies, researchers are uncovering methods to potentially enhance microglial activity against Alzheimer’s-related plaques.
Moreover, the transition from cancer immunotherapy to Alzheimer’s treatment reflects a crucial paradigm shift in understanding neuroinflammation and its management. The role of TIM-3 in both scenarios underscores a common pathway where immune checkpoints modulate the body’s ability to respond to detrimental accumulations, whether in tumor cells or amyloid plaques. This translational research can potentially yield therapeutic breakthroughs that improve outcomes for patients struggling with the cognitive decline associated with Alzheimer’s, mimicking successful interventions seen in oncology.
Gene Polymorphisms and Their Role in Alzheimer’s
Genetic factors significantly influence the manifestation of Alzheimer’s disease, with polymorphisms in genes like TIM-3 demonstrating a noteworthy connection. Studies have shown that individuals with particular TIM-3 gene variations exhibit heightened susceptibility to late-onset Alzheimer’s due to differences in microglial function. These polymorphisms not only affect the expression of TIM-3 on microglial cells but are also implicated in an individual’s overall immune response to amyloid beta buildup.
By understanding how TIM-3 gene variations contribute to Alzheimer’s pathology, researchers can tailor targeted therapies that consider genetic backgrounds. Identifying high-risk individuals through genetic screening opens pathways for early intervention, potentially leading to proactive strategies in managing the disease even before significant cognitive decline occurs. Continued exploration of gene polymorphisms presents an exciting frontier in optimizing personalized Alzheimer’s treatment.
Impact of Neuroinflammation on Alzheimer’s Progression
Neuroinflammation is a central player in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease, significantly affecting cognitive function and brain health. Chronic inflammation, often facilitated by activated microglia and the expression of molecules like TIM-3, leads to neuronal damage and synaptic loss. As the immune response becomes maladaptive, it creates a cycle of inflammation that not only contributes to plaque formation but also exacerbates the loss of neuronal function.
Research into neuroinflammation suggests that managing inflammatory processes could provide therapeutic benefits in Alzheimer’s care. Strategies aimed at inhibiting excessive microglial activation or enhancing their plaque-clearing abilities could break the cycle of neuroinflammation and promote cognitive resilience. Understanding the dynamics of neuroinflammation is vital for developing therapies that successfully mitigate the effects of Alzheimer’s disease, thereby opening doors to improved patient outcomes.
Cognitive Recovery in Alzheimer’s Models
Exploring cognitive recovery in mouse models of Alzheimer’s provides insights into potential therapeutic avenues for human applications. In studies where TIM-3 was genetically deleted, notable improvements in cognitive functions were observed, indicating that alleviating microglial inhibition can enhance memory and learning capabilities. These experiments demonstrate the capacity for cognitive comeback, which is particularly relevant given the challenges faced by traditional Alzheimer’s interventions.
Such research emphasizes the importance of understanding not only how to halt disease progression but also how to rejuvenate lost cognitive functions. The applications of TIM-3 therapy in restoring cognitive health could prove transformative, changing the way Alzheimer’s disease is perceived and treated. Continued exploration into the mechanisms of cognitive recovery will be essential as researchers look to translate these findings into viable treatments for affected individuals.
Future Perspectives on Alzheimer’s Research
Looking ahead, the future of Alzheimer’s research hinges on advancements in immunological approaches, particularly those invoking TIM-3 and other checkpoint molecules. Given the historically limited success of traditional Alzheimer’s therapies, there is a pivotal need for innovative strategies that can effectively target the immune side of the disease. By repurposing existing therapies from cancer treatment, researchers are poised to break new ground in the fight against Alzheimer’s.
Incorporating strategies that target TIM-3 within microglia not only holds promise for improving clinical outcomes but also deepens our understanding of the disease pathology. Continuous collaboration between neuroscientists, immunologists, and geneticists will be crucial in developing comprehensive treatment approaches. With ongoing research efforts focused on TIM-3 memory restoration strategies, there is optimism that the next generation of interventions may pave the way for significant breakthroughs in Alzheimer’s care.
The Role of Anti-TIM-3 Antibodies in Treatment
The therapeutic use of anti-TIM-3 antibodies offers a promising front in Alzheimer’s treatment, utilizing an approach familiar from cancer immunotherapy. By blocking the inhibitory effects of TIM-3 on microglia, these antibodies can potentially restore the natural immune response within the brain, allowing for enhanced clearance of amyloid beta plaques that compromise cognitive function. This targeted therapy may represent a paradigm shift in managing neurodegeneration associated with Alzheimer’s.
As researchers work to identify and test candidate anti-TIM-3 antibodies for their effectiveness in mouse models, the implications of such treatments could be profound. If successful, these approaches could lead to new clinical trials in human subjects, bringing hope to millions affected by Alzheimer’s disease. By aligning cancer treatment strategies with neurodegenerative disease management, there’s significant potential for developing innovative solutions that change the landscape of Alzheimer’s therapy.
Clinical Translation of TIM-3 Research
The transition from basic research findings on TIM-3 to clinical application is marked by a multifaceted approach involving rigorous testing and patient trials. As understanding of TIM-3’s role in Alzheimer’s deepens, researchers are forming strategies that include human-related studies utilizing models with inserted human TIM-3 genes. This direct connection to human biology will be crucial in evaluating how anti-TIM-3 therapies can effectively target amyloid plaque clearance and cognitive restoration.
Furthermore, the collaboration among various research institutions signifies a robust commitment to advancing Alzheimer’s therapy based on TIM-3 studies. Efforts to secure funding and resource allocation are vital for conducting extensive clinical trials. Observing real-world outcomes from these trials will not only inform best practices but also create a pathway for more comprehensive care approaches tailored to the needs of Alzheimer’s patients.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is TIM-3 therapy for Alzheimer’s disease?
TIM-3 therapy for Alzheimer’s disease involves the use of anti-TIM-3 antibodies or small molecules that inhibit the TIM-3 protein. This approach aims to reactivate immune cells called microglia, allowing them to clear amyloid plaques, which are harmful accumulations in the brain associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
How does TIM-3 immune checkpoint affect Alzheimer’s treatment?
The TIM-3 immune checkpoint limits the activity of microglia, preventing them from effectively clearing amyloid plaques in the brain. By blocking TIM-3, researchers aim to enhance the immune response against these plaques, potentially leading to improved cognitive functions in Alzheimer’s patients.
What role do microglia play in Alzheimer’s and how does TIM-3 affect them?
Microglia are the brain’s immune cells, crucial for maintaining brain health and clearing debris like amyloid plaques. In Alzheimer’s disease, TIM-3 is overexpressed on microglia, which inhibits their ability to engulf and clear these plaques, thus contributing to disease progression.
Can TIM-3 therapy improve cognitive functions in Alzheimer’s patients?
Preliminary studies in mice have shown that TIM-3 therapy may improve cognitive functions by enhancing microglial plaque clearance. As a potential therapy for Alzheimer’s, blocking TIM-3 might restore some memory functions by reducing plaque accumulation in the brain.
What is the significance of TIM-3 as a genetic risk factor for late-onset Alzheimer’s?
TIM-3 has been identified as a genetic risk factor for late-onset Alzheimer’s disease due to its polymorphism linked to the condition. This suggests that variations in the TIM-3 gene may influence the disease’s onset and progression, making it a target for therapeutic strategies.
How does TIM-3 relate to neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease?
TIM-3 contributes to neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s by inhibiting the actions of microglia, which are essential for clearing plaques. Increased TIM-3 expression can lead to chronic neuroinflammation, worsening cognitive decline associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
What are the implications of using cancer treatment strategies like TIM-3 therapy for Alzheimer’s disease?
Utilizing cancer treatment strategies such as TIM-3 therapy for Alzheimer’s disease presents an innovative approach. These therapies, already effective in oncology, may help redirect the immune system to combat Alzheimer’s pathology, thereby improving symptoms and disease management.
What future research is planned for TIM-3 therapy in human Alzheimer’s disease?
Future research involves testing humanized anti-TIM-3 antibodies in mouse models that mimic Alzheimer’s disease. This will help determine their efficacy in halting the development of amyloid plaques, providing insight into potential clinical applications for human patients.
| Key Points |
|---|
| TIM-3 therapy could help treat Alzheimer’s disease. |
| TIM-3 is an immune system molecule that inhibits microglial activity in the brain. |
| Inhibiting TIM-3 allows microglia to attack and clear amyloid plaques, improving cognition in mice. |
| Most Alzheimer’s cases are late-onset, affecting 90-95% of patients. |
| The research showed that deleting TIM-3 could enhance memory retention in mice with Alzheimer’s-like symptoms. |
| Next steps include testing human anti-TIM-3 antibodies in mouse models. |
Summary
TIM-3 therapy for Alzheimer’s is showing promising potential as a strategy to overcome the obstructions posed by immune system checkpoint molecules in the brain. Recent studies have indicated that inhibiting TIM-3 can enable microglia to effectively clear amyloid plaques, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s, thereby improving cognitive functions in mice. This innovative approach not only targets the underlying pathology of the disease, but also represents a significant departure from traditional treatments that have failed to yield substantial results. As research progresses, there’s hope that TIM-3 therapy can be adapted for human treatment, potentially offering new avenues for combatting this debilitating condition.